SEBI has mandated all the fund houses to label their products for risk. There are two labels
1) Risk-o-meter : It indicates the current risk level of the scheme
2) PRC matrix : Maximum risk the fund manager can take in the scheme
In any debt fund there are two types or risk:
Interest Rate risk
Interest rate risk is the risk that the value of a bond will change due to changes in the level of interest rates. When interest rates rise, the value of bonds tends to fall, because people will be more willing to buy new bonds that are getting issued at higher rates. Conversely, when interest rates fall, the value of bonds to rise.
Credit Risk
Credit risk refers to the risk that a borrower may default on the principal and interest payments.
Lets understand Potential Risk Class (PRC) of a debt fund in detail:
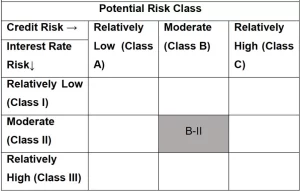
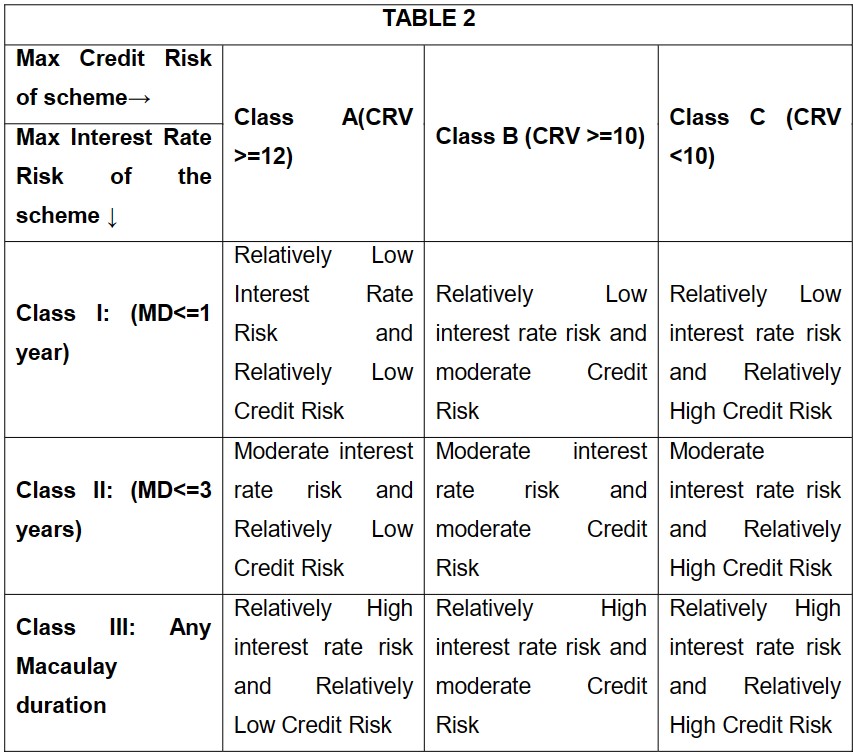
SEBI has classified interest rate risk into 3 categories:
- Class I: MD<= 1 year;
- Class II: MD<=3 years;
- Class III: Any Macaulay duration
Macaulay duration is used to help investors understand the sensitivity of a bond prices to changes in interest rates.
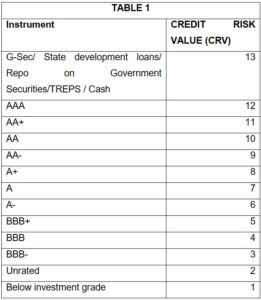
SEBI has classified Credit Risk into 3 categories:
- Class A: CRV >=12
- Class B: CRV >=10
- Class C: CRV <10
Takeaway, you must take a look at the maximum risk a fund can take and if it aligns with your investment objective before investing in any debt funds. For understanding how to analyse a bond fund you can refer Know These Factors Before Investing in a Bond Fund – My Invest Buddy. You can also consult Consult Us – Mutual Fund Advisor and other Investment Advisory – My Invest Buddy, we will create a personalized investment plan for you based on your investment objective.
References:
SEBI | Circular on Potential Risk Class Matrix for debt schemes based on Interest Rate Risk and Credit Risk
SEBI| Circular on Product Labeling in Mutual Fund schemes – Risk-o-meter
Join our community over at Instagram and Facebook

